One Way Hash Functions and Length Extension Attack
The basic building block of cryptography is one-way hash functions. The main feature of One way hash functions is that they are One Way and collision resistant.
The one-way feature is that the data itself cannot be calculated retroactively from the (summary) hash value of the data entered in the hashing process.
hash(m) = h, m is hard to find.
Collision resistant means that a hash value belongs to only one data. That is, a hash value cannot be common to two different data.
It’s hard to find m1 and m2 giving the same hash. hash(m1) = hash(m2)
The features of One Way Hash functions are generally as follows.
- Password authentication
- Integrity preservation
- Blockchain
Attacks to disrupt the functionality of one-way hash functions;
- Length Extension Attack
- Collision Attack
Common One-way Hash Functions: MD series and SHA series are hash functions
MD One-Way Hash Functions
MD (Message Digest) . Developed by Ron Rivest. Includes MD2, MD4, MD5 and MD6
States of Algorithms:
- MD2, MD4 — severely broken (outdated old)
- MD5 — collision resistance feature is broken, one-way feature is not broken
- MD6 — Developed in response to recommendation by NIST
SHA
Published by NIST. It includes SHA-0, SHA-1, SHA-2, and SHA-3.
States of Algorithms:
- SHA-0: retracted due to flaw.
- SHA-1: Designed by the NSA; Collision attack was found in 2017.
- SHA-2: Designed by the NSA; Includes SHA-256 and SHA-512
- SHA-3: Released in 2015; It has different structure plan (according to SHA-1 and SHA-2)
When calculating the MD5 hash, the data is divided into certain parts, and a 128-bit summary data is created by processing according to the md5 algorithm.
Application Areas of One Way Hash Functions
- Integrity Verification
- Committing a Secret Without Telling Itek)
- Password Verification
- Trusted Timestamping
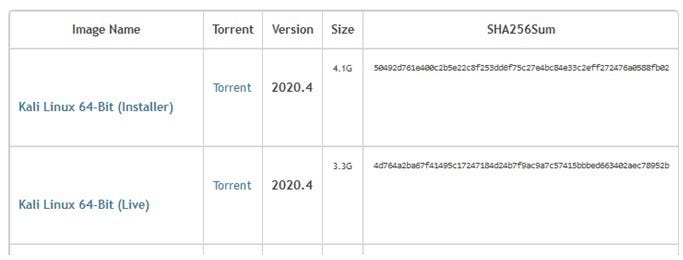
Integrity Verification: It is used to find out if a file has been modified or corrupted. For example, if the hash value given to us while downloading a file from a site is the same as the hash value we have produced from the downloaded file, we determine that the two files are exactly the same. Because even if there is a one-bit change in the file, a very different hash value is obtained.
Checksum value on Kali Linux distribution download page
Get Kali | Kali Linux
A Kali Linux Live image on a CD/DVD/USB/PXE can allow you to have access to a full bare metal Kali install without…
www.kali.org
Committing a Secret Without Telling It: One of the biggest benefits of One hash functions is that it allows a secret to be processed before it is revealed. It doesn’t make sense for a hash value to be exposed because the original data that has been digested from that hash value cannot be accessed. However, this hash value can be used to prove something.
For example, you made a prediction about the future values of some shares in the stock market, and you took the hash value of this prediction file and shared it with the people you want to prove your claim. But you don’t want these people to learn the estimated values in advance and buy the shares. So only the hash value is shared. When the time specified in the stocks has passed, we give the file containing the share values to the people we share it with to prove our claim. They generate the hash value of this file and check it with the hash value given to them beforehand, thus verifying that it is a written file with their predictions beforehand.
Password Verification: To enter an account, the user must enter a password. These passwords should not be stored unencrypted as plaintext for security reasons. For this, the passwords are hashed and stored in the database in this way. When the user logs in, the hash of the entered password is taken and the password is verified by checking the hash in the database. In Linux, passwords are stored as hashed in the /etc/shadow file.

The stored hash in Linux is as in the picture. The first $6 value represents the hash type. The next salt portion is intended to slow the brute force attack by adding a hash value plus a hash value to the current hash.
$1 = MD5 hashing algorithm.
$5 =SHA-256 Algorithm
$6 =SHA-512 Algorithm
Purpose of Salt: When using salt, the same input can result in different hashes.
- Password hash = one-way hash rounds (password || random string) -> it is generated with a random string value when generating the hash value.
- It’s just a random string value.
The salt value must be different for each user and must be hashed and stored.
Attacks Prevented by Salt
- Dictionary Attack: Possible password (commonly used passwords, name, surname, phone numbers, etc.) is stored in a file and the hash value is taken for each word, compared with the password hash and the password is tried to be decrypted.
- Rainbow Table Attack: Possible passwords are kept in the table with their pre-prepared hash values. The difference from the Dictionary attack is that the hashes of possible words are found in the file and the password hash is checked directly with the hash in the file. In this way, the hash value is not calculated for each password during the check, it saves processing power and is effective in small-sized jobs.
How Does Salt Prevent These Attacks?
- If the Target password is the same as the previously calculated data, the hash will be the same.
- If this property (same hashes) is not valid, all previously calculated data is useless.
- By adding extra data to the pure hash value, it destroys the feature of having these hash values the same.
Trusted Timestamping: It arose out of the need to prove how a document existed before a certain date.
- Timestamping Approaches: There are 3 types of approaches.
- Approach #1: By publishing a One-Way Hashi (rather than a document) in a newspaper or magazine.
- Approach #2: The Time Stamping Authority (TSA –Time Stamping Authority-KamuSM-TUBITAK) can sign the hash using the private key. Timestamp is accepted as legal evidence in Turkey. It can be used as a proof document in proof of copyright by being recorded with a timestamp in the files containing the offer right.
- Approach #3:
- Use blockchain i.e. a growing list of records (blocks)
- Publish the hash document on a blog
- Blockchain depends on one-way hash
Message Authentication Code (MAC)
- Network communication may encounter MITM(Man-in-the-middle) attacks. In a MITM attack, a third person can enter between the two communicating parties and pass the communication over himself, and in this way, he can manipulate the communication by changing religions.
- MITM can capture and manipulate data
- The receiver is required to verify the integrity of the data (whether the data has been modified).
- Add tags to data
- Using the one-way hash as a tag won’t work because MITM can recompute the hash.
- A secret (key) must be used in the hash, which is shared between the sender and the receiver.
- MITM cannot compute hash without secret key
Length Extension Attack on MAC
While hashing, the hash value processed in one block is used in the other hash operation (length extension).
Using the length extension feature, a valid MAC can be created without knowing the secret key.
Switched HASH MAC (HMAC)
- It uses the hash function H (compression function block size B) and a secret key K.
- Can be used with any one-way hash function
HMAC does not encrypt the message to be sent. Instead, the message is transmitted along with the HMAC digest. The party that knows the secret key takes the hash of the message again and compares it with the hash sent with the message. If the new hash obtained matches the hash sent with the message, the message is verified.
Blockchain and Bitcoins
- An ever-growing list of records called a block
- Managed by ledgers (records) in a peer-to-peer network
- The accepted ledger block is difficult to change because it requires replacing all subsequent blocks
- Popular app is Bitcoin
- Topics we will cover:
- Hash Chain and Blockchain
- Make Chaining Difficult
- Adding Incentives and Bitcoin
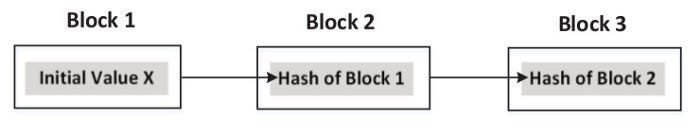
Hash Chain
- One-way hash function is repeatedly applied to a piece of data.
- If a block is modified, it will fall off the chain and will not be considered part of the chain.
- If the original data is changed, the whole chain needs to be rebuilt.
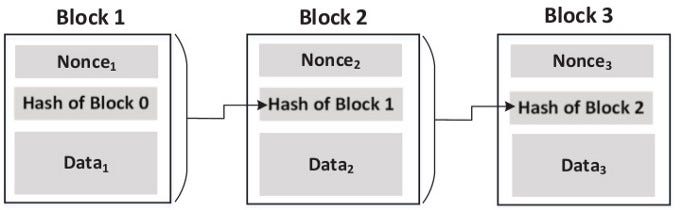
Blockchain
- Similar to hash chain, but contains additional information in each block
- Bitcoin example: blocks contain information about bitcoin transactions
- Chaining : Hash value of one block is inside the next block
- If a block is changed:
- All chains after this block are broken
Requires the need to re-chain all subsequent blocks

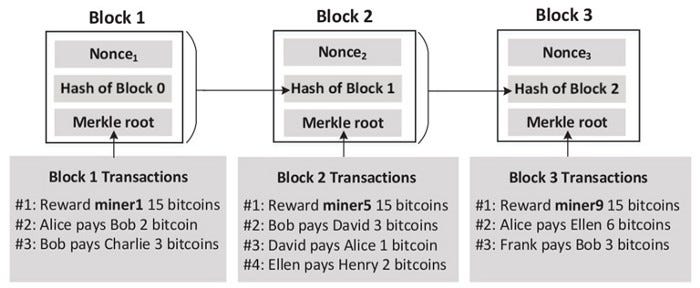
Blockchain: Make Chaining Difficult
- Nonce(Number Only Used Once) is added to each block
- The block hash must meet the requirement (e.g. 20 leading zeros)
- The number of leading zeros intentionally increases over time, as computational power will increase over time.
Blockchain Incentives (Incentive) and Bitcoin
- Provide bitcoin to anyone who can find nonce in chain blocks
- people/companies calling nonce are “miners”
Security Impact of Collision Attacks
- Forgery of public-key certificates
- Assume two certificate requests for www.example.com and www.attacker.com have the same hash due to conflict
- The CA(certificate authority ) signature of one of the two requests will be equivalent
- An attacker can retrieve the signed certificate for www.example.com without owning it
- Integrity of Programs
- Ask the CA to sign the hash of a legitimate program
- The attacker creates a malicious program with the same hash
- Legitimate program certificate also valid for malicious version
- These two examples are theoretical and their applicability is questionable.
Creating Two Different Files with the Same MD5 Hash
- The md5collgen tool creates two files with the same prefix (prefix )

In this attack, we will create two different files with the same MD5 hash values. The starting parts of these two files must be the same, meaning they share the same prefix. We can achieve this using the md5collgen program, which allows us to provide a prefix file with any arbitrary content.
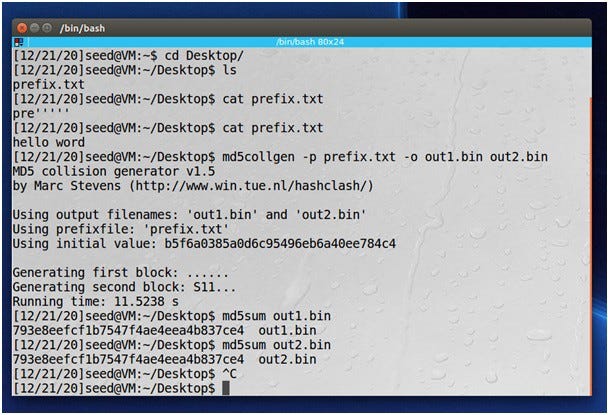
The following command creates two output files out1.bin and out2.bin,
prefix.txt for a specific prefix file:
We can check if the output files are different using the diff command. We can also use
md5sum command to check the MD5 hash of each output file.
$ md5sum out1.bin
$ md5sum out2.bin
Because out1.bin and out2.bin are binary, we cannot view them using a text viewer program,
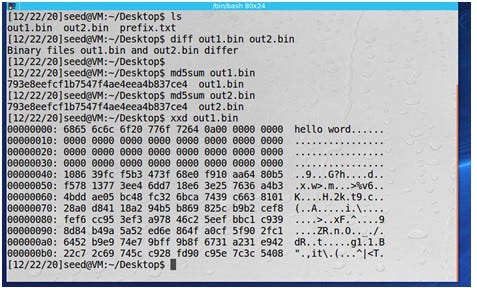
From the hex dump, it seems that the prefix.txt data is padded with zeros first, and then random-looking data is appended to it. The Out2.bin file has the same header but differs slightly in the remaining bytes.

- The information on this page has been prepared by using the information in the slides and files at https://www.handsonsecurity.net/resources.html. For more detailed information, please refer to the relevant address.

Son yorumlar